Are you curious about natural, nature-identical, and artificial flavourings in food? This comprehensive article will guide you through the differences and similarities between these flavourings, their impact on food, and their safety. Get ready to explore the world of flavours in your favourite dishes!
Introduction
Food flavouring is a fascinating subject that brings joy to our taste buds. In this article, we will delve into the three main types of flavourings used in the food industry: natural flavouring, nature-identical flavouring, and artificial flavouring. We’ll discuss what sets them apart, how they are produced, and any safety considerations. So, let’s embark on this flavour-filled journey!
What is Natural Flavouring?
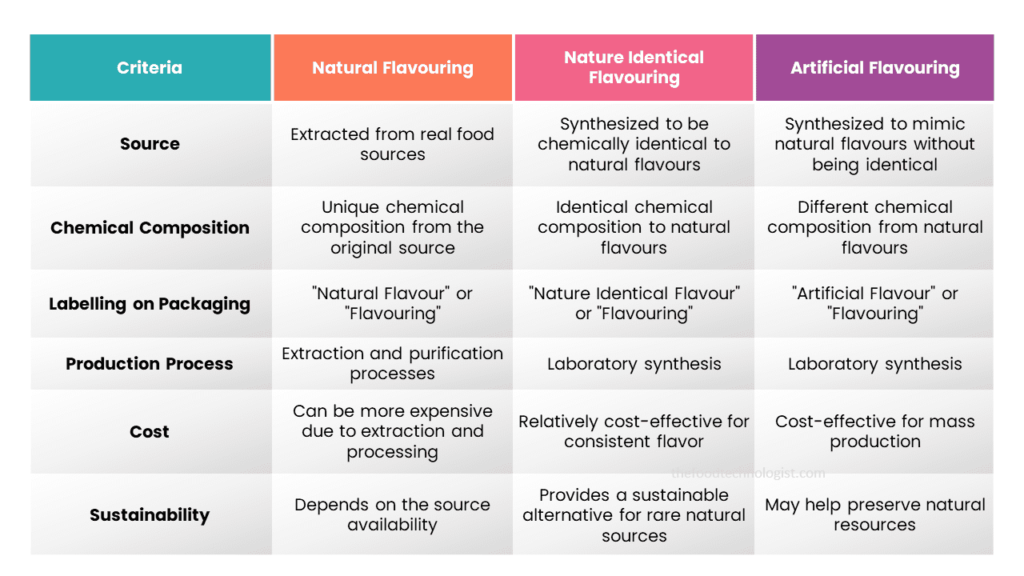
Natural flavouring is derived from real food sources, such as fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. These flavours are extracted through various processes to capture the essence of the original ingredient. When you see “natural flavour” listed on a food label, it means that the flavouring agent comes from a natural source, but it may undergo some processing for practical purposes. For example, natural strawberry flavouring could be derived from real strawberries, but it might go through filtration and purification to remove any impurities.
Exploring Nature Identical Flavoring
Nature-identical flavouring is synthesized in a lab to mimic the exact chemical composition of the flavour compound found in nature. These flavourings are chemically identical to those found in natural sources. When you consume a food product with “nature identical flavour” on the label, it means that the flavouring agent is the same as the natural one, but it was created in a controlled environment. This process ensures consistency in flavour and can be a more sustainable alternative when certain natural sources are scarce or expensive.
Unveiling Artificial Flavoring
Artificial flavouring is also synthesized in a lab, but it does not replicate the exact chemical composition of natural flavours. Instead, it is designed to mimic the taste of natural ingredients without being chemically identical. Artificial flavourings can be more cost-effective than natural or nature-identical flavours, making them a popular choice for mass-produced foods.
Key Differences Between Natural, Nature Identical, and Artificial Flavouring in Food
Now that we’ve introduced each type of flavouring let’s compare them side by side:
Common Misconceptions About Flavorings
There are some misunderstandings surrounding flavourings that need clarification. Many consumers assume that natural flavours are always healthier, which is not necessarily the case. Health aspects depend on the overall composition of the food product, not just the flavouring.
Another common misconception is confusing nature identical flavours with artificial flavours. Nature-identical flavours are created to be chemically identical to natural flavours, whereas artificial flavours are designed to evoke a general taste.
Safety Considerations for Flavourings in Food
Regarding the safety of flavourings in food, regulatory agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) play a crucial role in assessing their use. Both natural and artificial flavourings must undergo rigorous testing before they are approved for use in food products. The primary focus is on determining their safety for human consumption at various levels.
The use of flavourings in the food industry is regulated by various authorities to ensure consumer safety and product transparency.
- FDA and GRAS: In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the safety and labelling of flavourings. Many flavouring substances are designated as “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS), indicating that they are safe for consumption under specified conditions.
- International Standards: Other countries and regions have their own regulatory bodies and standards for flavourings. The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) is an international organization that evaluates the safety of food additives, including flavourings.
Food manufacturers must adhere to these regulations and use approved flavouring substances in their products. Additionally, they must accurately label their products to inform consumers of the presence of flavourings.
Nature-identical flavourings, being chemically identical to natural flavours, are generally considered safe as well. However, there can be exceptions when specific components of the flavour compound pose health concerns, even in trace amounts. Nonetheless, the level of scrutiny and testing for flavourings ensures that they meet safety standards and pose no significant health risks when consumed in moderation.
The Role of Flavourings in Various Food Products
Flavourings have a broad application across the food industry, enhancing the taste and appeal of a wide range of products.
- Beverages: Whether it’s soft drinks, juices, or alcoholic beverages, flavourings play a significant role in defining the taste. From classic cola to exotic fruit blends, the diversity of beverage flavours owes much to the work of flavorists.
- Snacks and Confectioneries: From potato chips to candies, snacks and confectioneries rely heavily on flavourings to create enticing taste profiles. Flavorists often create unique combinations that make these treats irresistible.
- Ready-to-Eat Meals: In the fast-paced modern lifestyle, convenience foods are popular, and flavourings are essential to make them appetizing. Ready-to-eat meals, soups, and frozen dinners all benefit from well-crafted flavourings.
- Baked Goods: The aroma of freshly baked bread or the delightful taste of cookies largely comes from the carefully selected flavourings used by bakers and food manufacturers.
The Future of Flavorings in the Food Industry
As technology advances, flavorists and food scientists are exploring innovative ways to enhance flavours and improve their applications in various food products. This includes encapsulation techniques that protect flavours during processing and cooking, ensuring that the taste remains consistent until consumed.
Moreover, the sustainable sourcing of flavourings will gain importance as consumers become more conscious of the environmental impact of food production. There will also be a focus on understanding the cultural nuances of flavour preferences to cater to diverse markets effectively.
FAQs about Natural, Nature Identical, and Artificial Flavouring
Q: Are natural flavourings healthier than artificial ones?
A: Not necessarily. While natural flavourings come from real food sources, they can still undergo processing and may not retain all the original nutrients. Artificial flavourings, on the other hand, are designed to mimic taste but don’t offer nutritional value.
Q: Can natural flavourings cause allergies?
A: Yes, they can. Natural flavourings come from real ingredients that could trigger allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. It’s essential to check food labels for potential allergens.
Q: Are nature identical flavourings better for the environment?
A: Yes, nature-identical flavourings can be more environmentally friendly as they reduce the demand for harvesting certain natural resources.
Q: Are there any regulations on flavourings in food?
A: Regulatory agencies like the FDA , FSSAI and EFSA carefully evaluate and approve flavourings for safe use in food products.
Q: Can artificial flavourings be harmful to health?
A: When used within approved limits, artificial flavourings are considered safe for consumption. However, excessive consumption of any food additive should be avoided.
Q: How do I know which flavouring is used in a product?
A: Food manufacturers are required to list the type of flavouring used on the product label. Look for terms like “natural flavour,” “nature identical flavour,” or “artificial flavour.”
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between natural, nature identical, and artificial flavorings is crucial for making informed food choices. Natural flavourings are derived from real sources, nature identical flavourings replicate the exact chemical composition of natural flavours, and artificial flavourings mimic taste without being chemically identical. All three types go through rigorous safety testing to ensure they are safe for consumption.
The next time you savour your favourite dish, take a moment to appreciate the intricate world of flavourings that make our culinary experiences so delightful.












Leave a Comment